UHF SATCOM STANAG 4681 Waveform Development
In 2020, Arke Telekom initiated a project with ASELSAN to implement the NATO STANAG 4681 UHF SATCOM waveform on the ASELSAN 9661-AG2 software-based radio. This development enabled the 9661-AG2 radio to communicate via satellite by simply installing new software and connecting a satellite antenna. The primary goal was to facilitate long-distance communication for military units dispersed over vast geographical areas where non-satellite communications are impractical. STANAG 4681 compatibility ensures interoperability with other NATO units over NATO satellites, enhancing coordination in joint operations. The project was completed by early 2022, with provisions to port the UHF SATCOM waveform to other ASELSAN software-based radios.
UHF SATCOM Satellite System
Geostationary SATCOM communication satellites orbit approximately 36,000 km above the Earth’s equator. Due to this distance, a UHF SATCOM satellite covers nearly a hemisphere, allowing communication between units spread over a wide area. However, this also results in a significant round-trip delay, varying between 239-279 ms depending on the unit’s location within the coverage area. In a UHF SATCOM network, the satellite does not store any control information; it merely performs channel separation, amplification, and signal relaying. Given the limited satellite bandwidth, efficient resource utilization is crucial. STANAG facilitates dynamic resource management through a central control unit on Earth, which monitors connection requests and allocates resources accordingly. Each unit connected to the network listens to and participates in control communication on a predefined frequency and time slot via the satellite’s order-wire (OW) service.
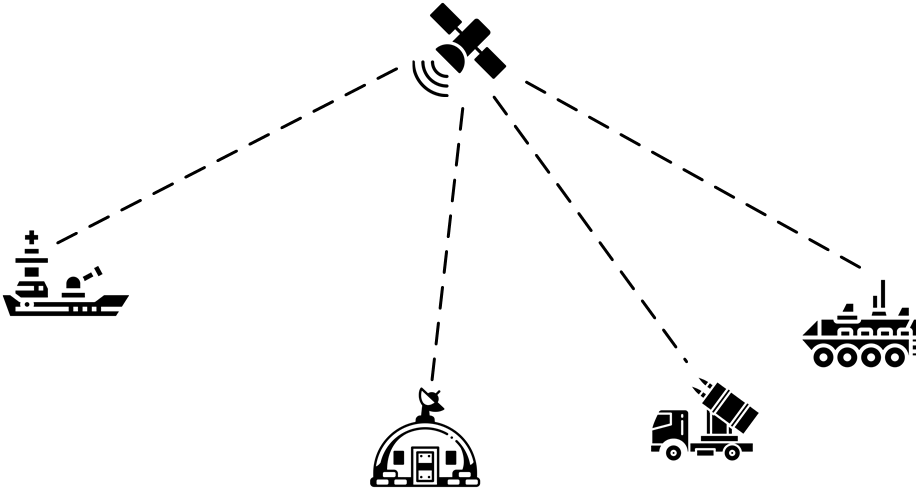
Tactical Field Satellite Communication Network
Dynamic Resource Management
Dynamic resource management is addressed through two methods:
-
Pre-Planned Services: Resources are assigned before system deployment, allowing for continuous services. During operation, resource assignments can be modified, services can be added or removed, and new members can be integrated into existing services. However, terminals cannot request services that are not predefined.
-
Ad Hoc Services and DAMA Protocol: When unplanned communication services are needed, the DAMA (Demand Assigned Multiple Access) protocol is employed. Scheduled pre-assigned services use the SFOW (Scheduled Fixed Order Wire) service located in the Master Channel, while DAMA control utilizes DFOW (Demand Fixed Order Wire) in the DAMA Control Channel. DROW (Demand Random Order Wire), UCOM (User Communication), and Ranging services can operate on all channels.
Multiple units share a satellite channel using the TDMA (Time Division Multiple Access) protocol. Additionally, a single access communication mode is supported, dedicating certain satellite channels for exclusive use by specific units.
Channel Controller (CC) and Alternate Channel Controller (ACC)
The Channel Controller (CC) is the central unit managing satellite resources. Terminals join the network and request resources from the CC. The Alternate Channel Controller (ACC) monitors control communications and can assume control if the CC becomes unavailable. The CC not only assigns resources but also monitors their utilization, reallocating unused resources as necessary. The ACC listens to all control transmissions to maintain an accurate database of ongoing services, ensuring a seamless transition if it needs to replace the CC.
Timing Requirements and Ranging
All terminals synchronize their timing with the CC’s transmissions. However, synchronization errors, Doppler shifts, or phase noise can cause clock discrepancies among units. Terminals must correct these variations to align with the satellite’s time frame. Ranging operations are conducted to achieve time synchronization, either passively using GPS data or actively by transmitting and receiving dummy signals to calculate time differences.
User Services
STANAG defines three types of user services:
-
Circuit Service: Provides fixed-rate voice and data transfer.
-
ADT (Asynchronous Data Transfer) Service: Supports fixed or variable-rate data transfer.
-
Block Assignment Service: Allows subdivision of an assigned time slot by higher-layer protocols for further multi-access purposes (optional feature).
The satellite network offers modern communication services, including point-to-point calls, conference calls, call joining/leaving, call pausing, service request queuing, waiting on busy terminals, and service prioritization. As a military system, it also supports features like encryption and silent mode (listener-only participation).
Variable Data Rates and Error Detection/Correction
The physical layer accommodates various terminals with different modulation capabilities under varying link quality conditions. A wide range of data rates is supported through various modulation types. The signaling protocol enables source and target units to agree on suitable transmission parameters based on actual channel quality. Control data fields are protected using CRC (Cyclic Redundancy Check) or RS (Reed-Solomon) codes.